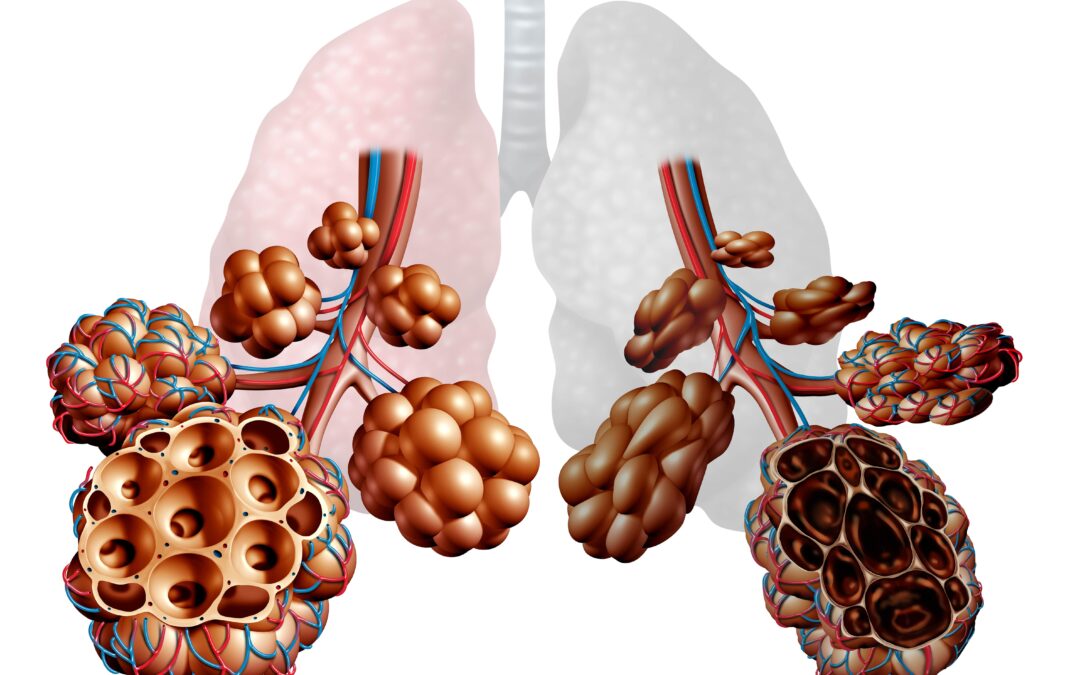
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in older adults. COPD is characterized by shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. The disease progresses over time, causing damage to the lungs and making breathing more difficult. COPD is a complex disease that requires a multifaceted approach to management. In this article, we will discuss strategies for managing COPD in older adults.
Medication Management:
The first step in managing COPD is medication management. There are several medications that are commonly used to treat COPD, including bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and oxygen therapy. Bronchodilators are medications that help to open up the airways in the lungs, making it easier to breathe. Corticosteroids help to reduce inflammation in the lungs, which can also improve breathing. Oxygen therapy is used to provide additional oxygen to the body, which can help to alleviate symptoms of COPD.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a program that is designed to help individuals with COPD improve their breathing and overall physical condition. Pulmonary rehabilitation includes exercise, breathing techniques, and education about the disease. It is an effective way to improve lung function and reduce symptoms of COPD. Pulmonary rehabilitation is typically done in a group setting, which provides social support and encouragement.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is the leading cause of COPD. It is important for individuals with COPD to quit smoking in order to slow the progression of the disease. Smoking cessation programs can be helpful for individuals who are struggling to quit smoking. These programs typically include counseling and support to help individuals quit smoking.
Nutritional Support
Nutrition plays an important role in managing COPD. Malnutrition is common in individuals with COPD, which can lead to muscle wasting and weakness. It is important for individuals with COPD to eat a well-balanced diet that includes adequate protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Nutritional supplements may be recommended for individuals who are unable to eat enough food to meet their nutritional needs.
Avoiding Triggers
Individuals with COPD should avoid triggers that can worsen symptoms. Common triggers include air pollution, cold air, and respiratory infections. It is important to take steps to avoid these triggers, such as wearing a mask when outside during times of high air pollution, staying indoors during cold weather, and washing hands frequently to avoid respiratory infections.
Support Groups
Living with COPD can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Joining a support group can provide individuals with COPD with the emotional support they need to cope with the disease. Support groups can provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, learn coping skills, and connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
Conclusion
Managing COPD in older adults requires a multifaceted approach that includes medication management, pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking cessation, nutritional support, avoiding triggers, and support groups. With the right strategies in place, individuals with COPD can manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. It is important for individuals with COPD to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their individual needs.

Recent Comments